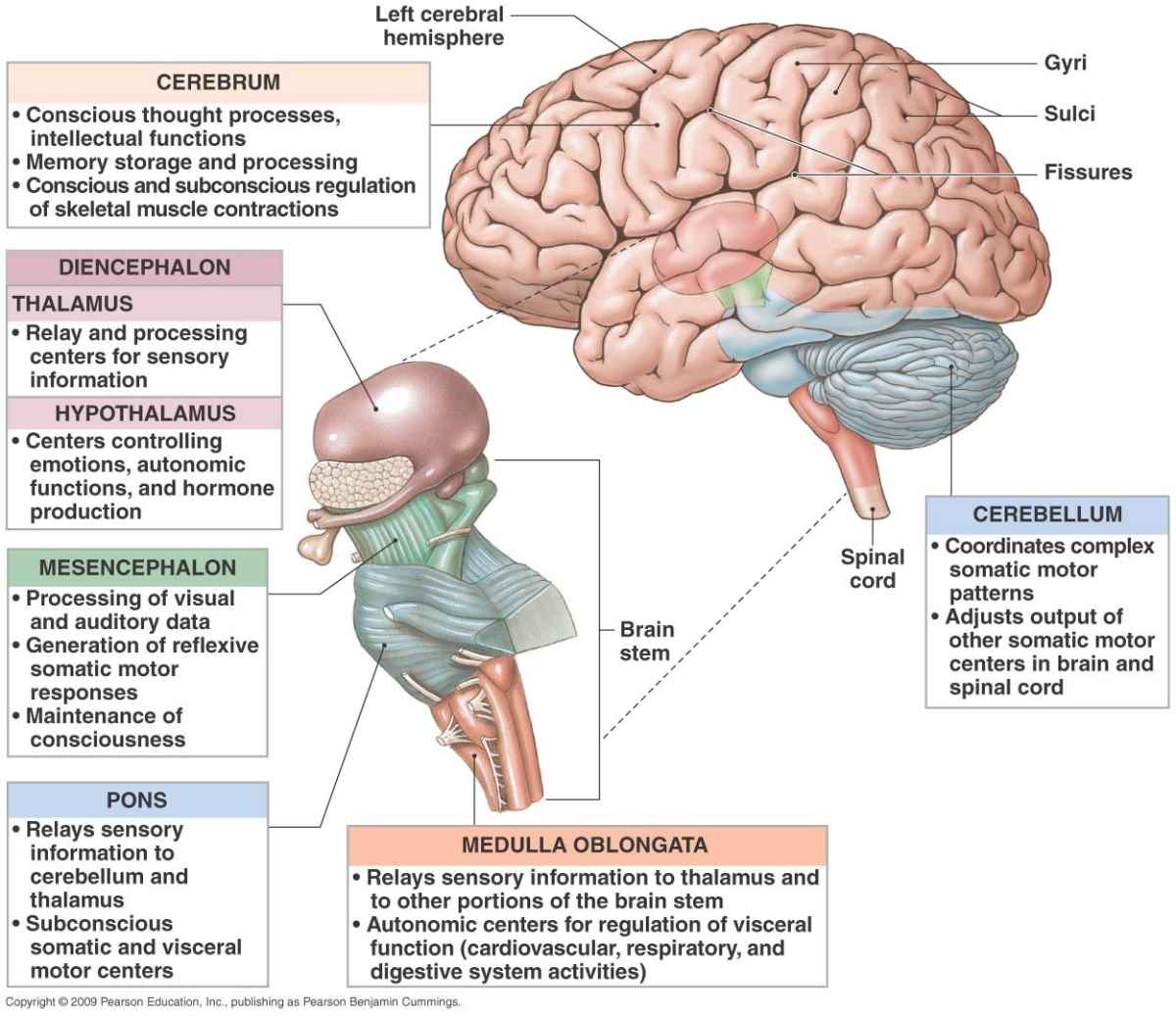
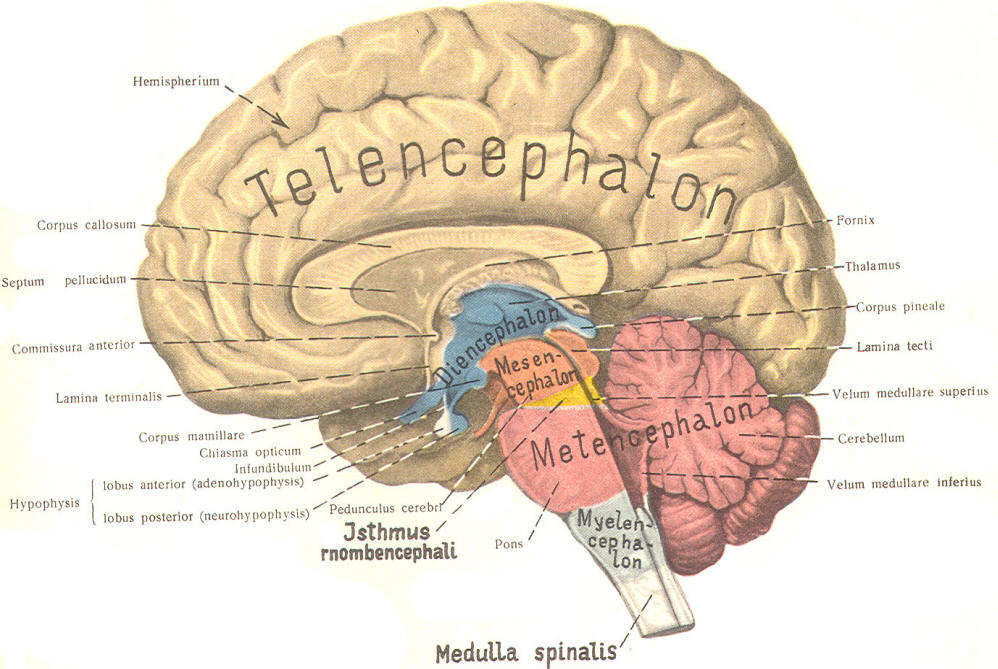
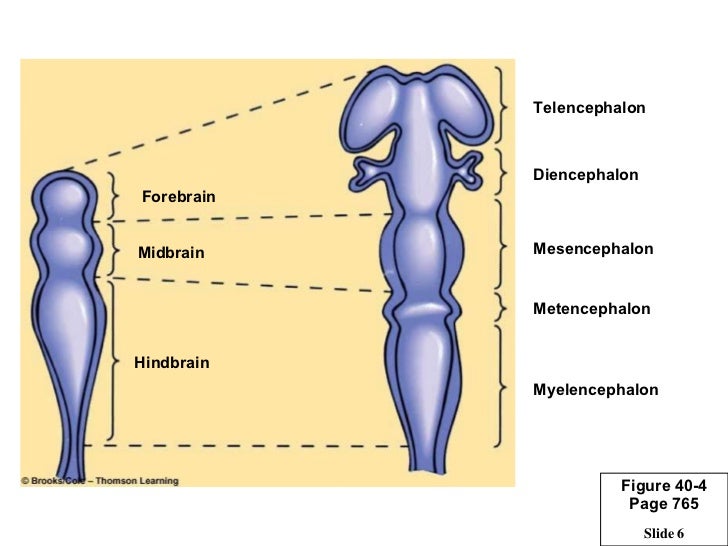
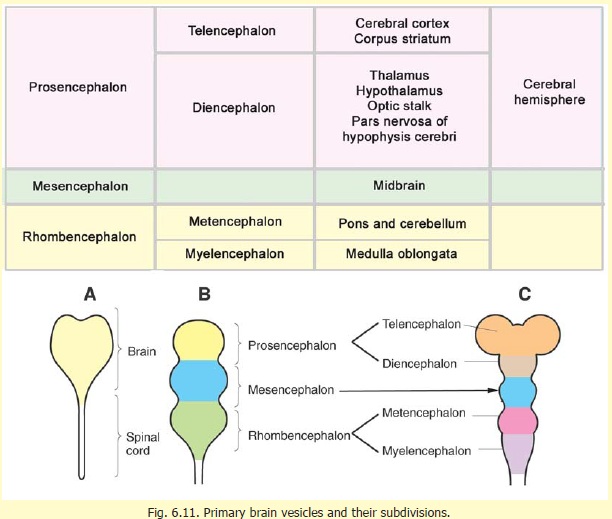
More specifically, it is divided into five major regions, namely, telencephalon, diencephalon or inter-brain, myelencephalon (hindbrain/medulla oblongata), metencephalon and mesencephalon (midbrain). Here follows a precise but comprehensive description of each of the above given divisions. Parts of the Human Brain and their Subdivisions. Abstract. Vertebrate brains commonly consist of five basic embryologic anatomical regions: telencephalon; diencephalon; mesencephalon; metencephalon; and myelencephalon. The proportions of these regions vary widely across species and developmental stages. Investigation of their growth trajectories, therefore, has the potential to provide an.

Parts of the Brain The Hindbrain (Myelencephalon & Metencephalon) — . 3iCreative

Divisions Of The Brain Prosencephalon Nervous System Neuroanatomy

Parts of the the Brain The Forebrain (Telencephalon & Diencephalon) — . 3iCreative

telencephalon, diencephalon, brainstem and spinal cord Brain drawing, Brain anatomy, Anatomy

The Five Major Divisions of the Brain. Forebrain Telencephalon Diencephalon Midbrain
Diencephalon

14.1 The brain develops four major regions the cerebrum, cerebellum, diencephalon, and brainstem
. Chordate anatomy. Chordata; Anatomy, Comparative. 350 CHORDATE ANATOMY Instead of only two
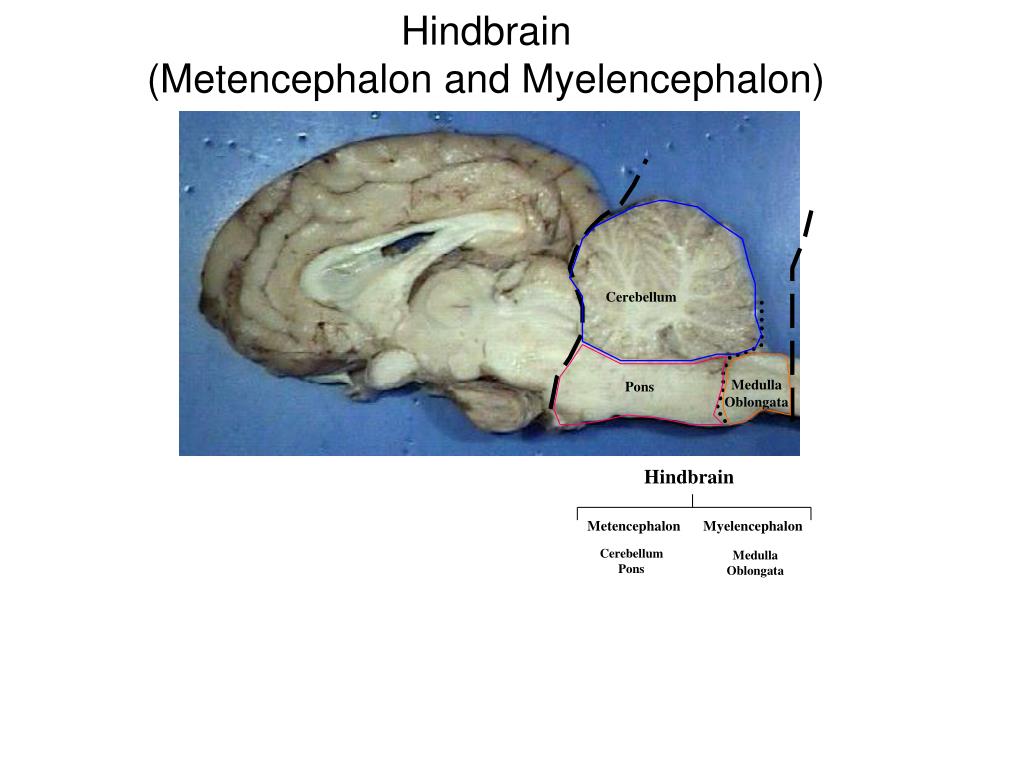
PPT Sheep Brain Dissection PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6058102
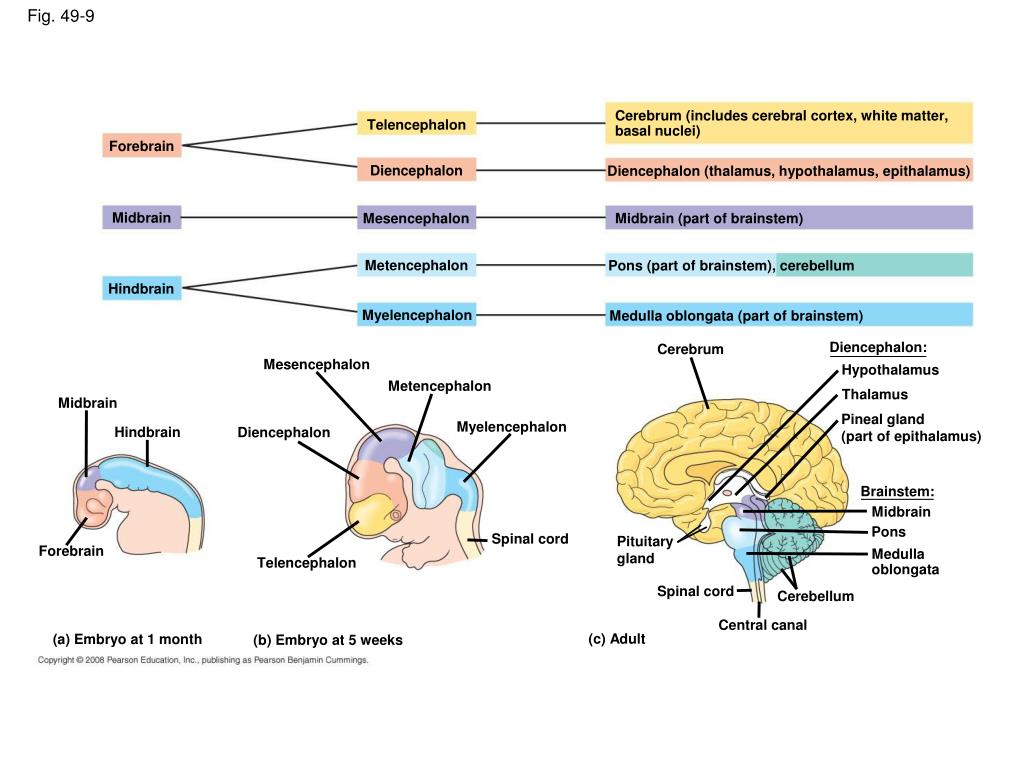
PPT Chapter 49 PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5568262

Brain Encyclopedia Anatomy.app Learn anatomy 3D models, articles, and quizzes

Pin on Neurodevelopment
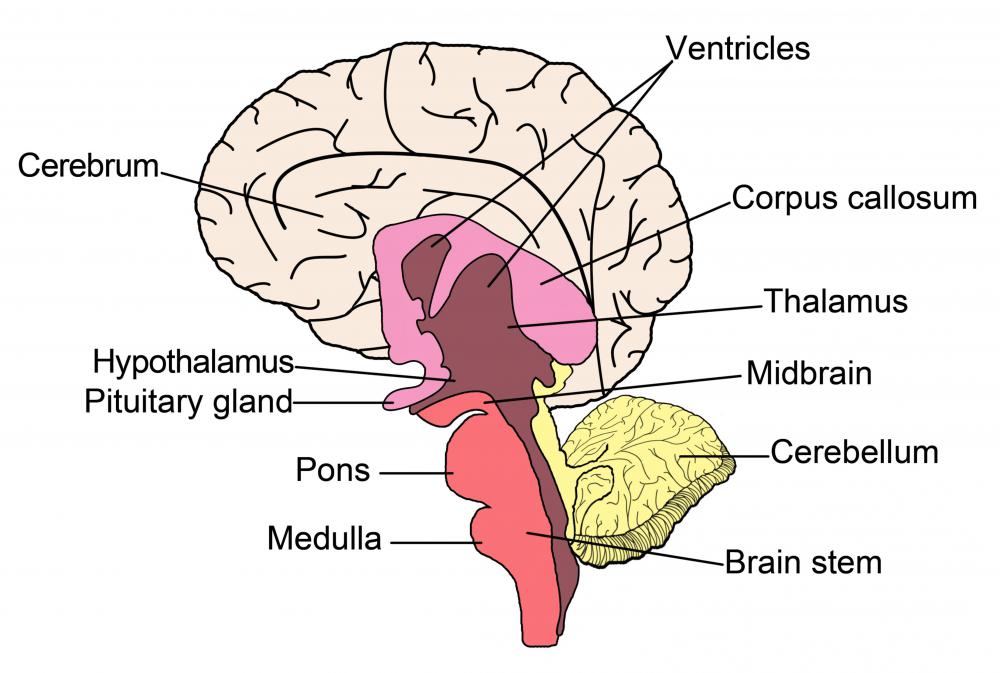
What is the Telencephalon? (with pictures)
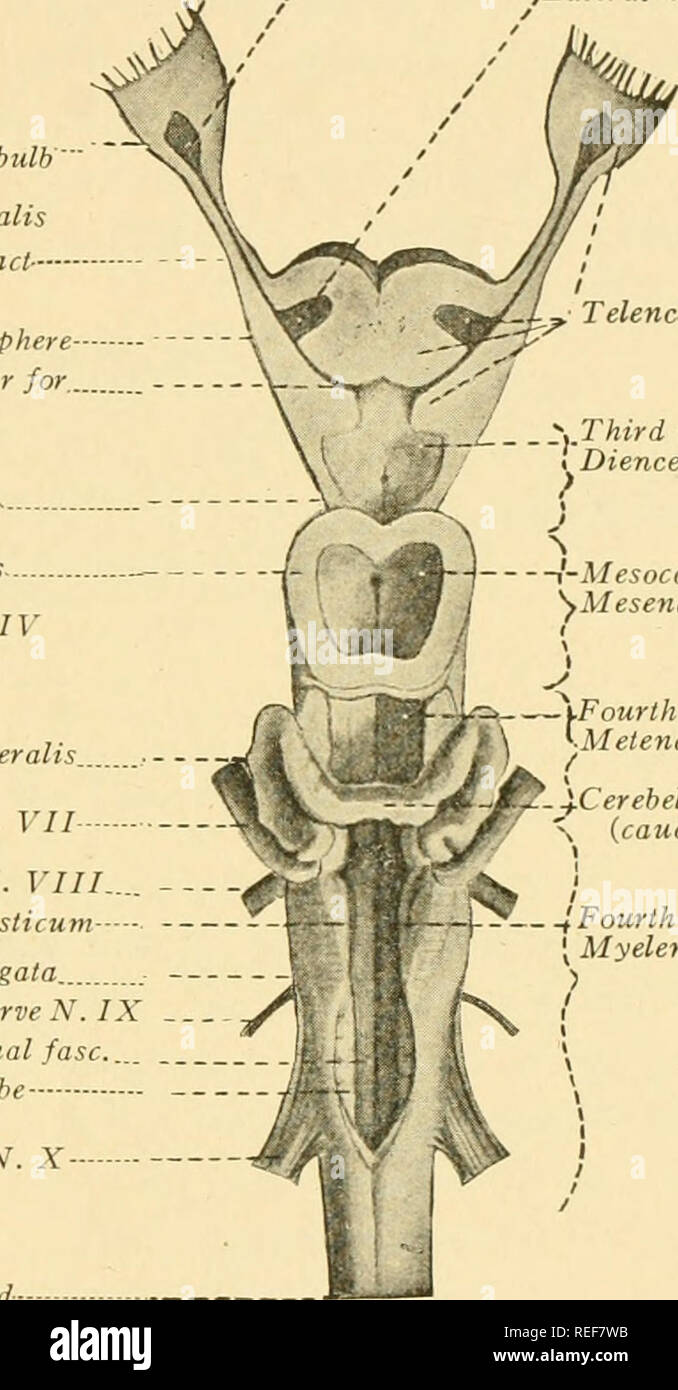
. La anatomía comparativa. Anatomía Comparativa. Lóbulos ópticos *^ Trochlear nervio N. I
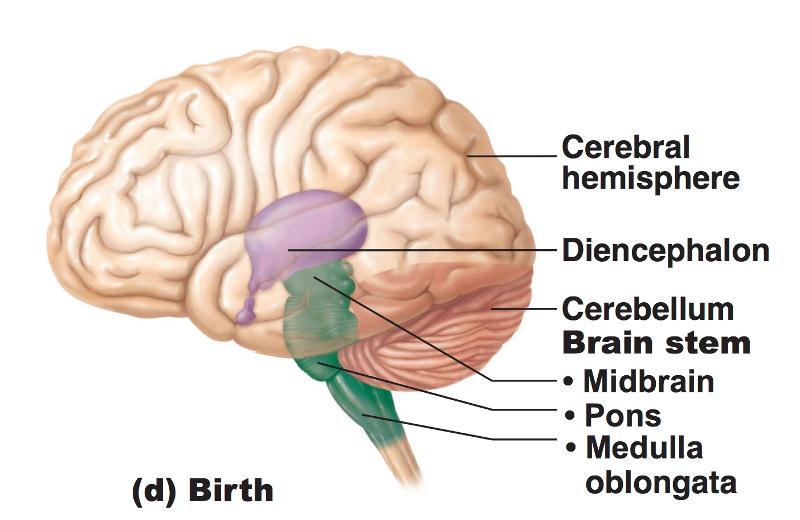
Print Chapter 12 The CNS (Brain and Spinal Cord) flashcards Easy Notecards
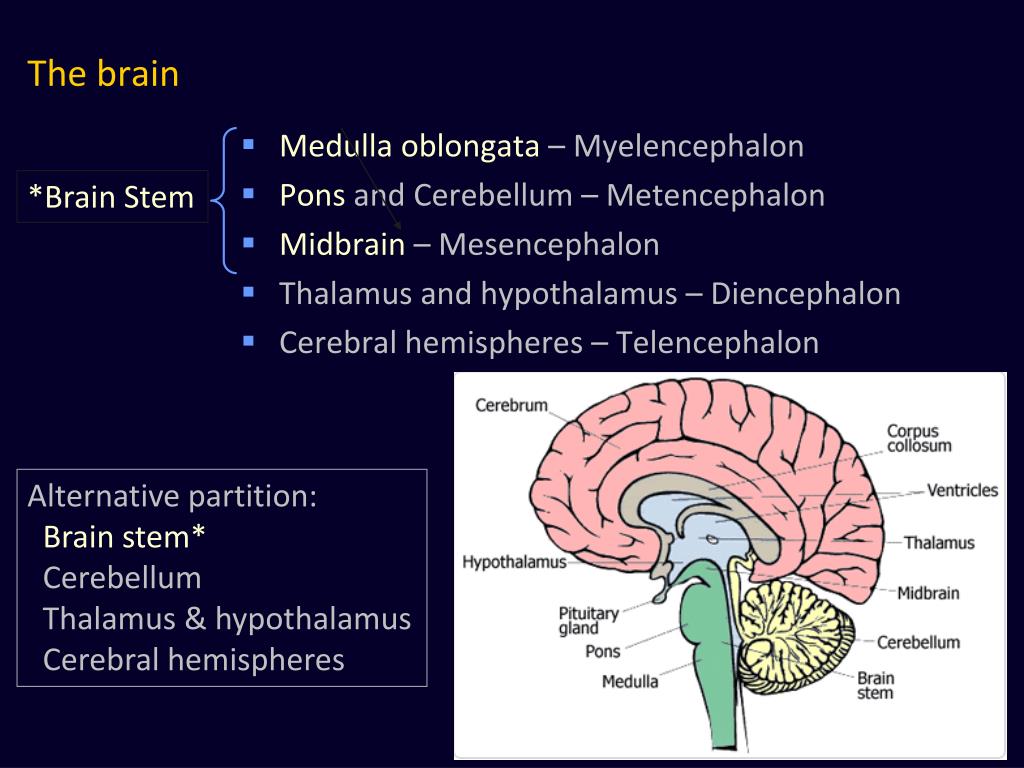
PPT II. Brain Structure PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID4829280
ERKUTLU SCIENCE CENTER NEUROEMBRIOLOGY
Regulacion nerviosa cap 41
Diencephalon Mesencephalon

Brain Structuresand functions review Diagram Quizlet
Telencephalon | Diencephalon | Mesencephalon | Metencephalon | Myelencephalon: Diencephalon. The diencephalon, which gives rise to the optic nerve, can be divided into four regions: thalamus, hypothalamus, subthalamus and epithalamus. A drawing of a median view of the rostral brainstem is shown below. Components of the diencephalon are labeled.. The prosencephalon subdivides into the telencephalon and diencephalon, with the optic vesicle extending from the border of the telencephalon and diencephalon. The rhombencephalon subdivides into the metencephalon and myelencephalon. The mesencephalon gives rise to the midbrain structures (Fig. 2)(Stiles et al., 2010; Kiecker and Lumsden, 2005).